Omni Directional Mobility
The
Mobile Robotics which operate on a floor or ground usually employ wheels. This is the case for Omni Directional Mobility drive.
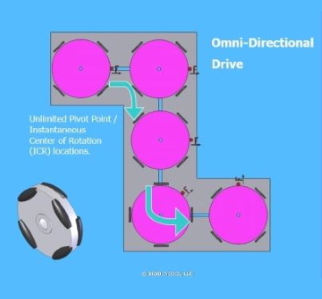
Omni-Directional Drive
The omni-directional mobility drive, Omni-drive vehicles for short, are considered holonomic but is in a class of its own.
The omni-drive module requires one motor per wheel module. The wheel modules are what provides the vehicle its unique maneuvering capacities. These modules operate using two DoF in the X-Y directions in a 3D work space; therefore, the individual wheel modules are not Holonomic.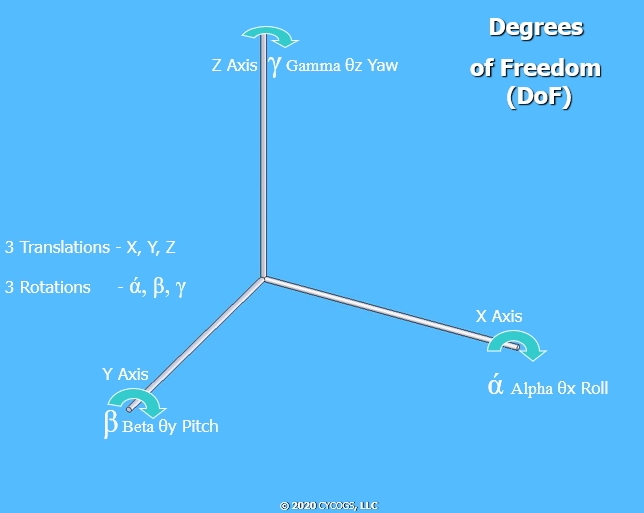
The omni-directional wheel modules are typically mounted at angles to each other as rotation of one-wheel module causes the rollers on the other wheel modules to rotate. The wheel modules are essentially rollers on a wheel module rim instead of the tire tread.

The omni-directional mobility systems are moreover known as the Mecanum wheel, Swedish wheel, Vuton wheel or the Spherical wheels.
These typically use fixed-mounting wheel modules with many small rollers as its treads, one propulsion motor per wheel. The effective wheel diameter is the diameter of the small rollers. The combination is very maneuverable, and is considered “Vector Controlled.”While an omni-directional equipped vehicle may satisfy the minimum definition of holonomic mobility,
some omni directional wheel drawbacks include: Limited traction, a very small surface contact patch, wheel slippage and induced movement errors, plus tread wear remain a problem and frequent wheel maintenance and repairs may be required.The omni-wheel vehicles are typically indoor systems, where dirt, grit, hair, carpet fibers remain an ongoing maintenance concern. For systems requiring a smooth, low vibration and precise positioning, the omni-wheel mobility drive should be designed and sized to remediate such issues as much as possible.
In this illustration, please notice the wheel itself, which is composed of several small rollers. From the illustrated movements, please note the F = Front designation. The omni-wheel can simulate synchronous mobility and holonomic movements. This is illustrated showing the front heading change.
 Learn more about AI Robotics with the
Learn more about AI Robotics with the The
Contact: Send questions and comments about this Education on Omni Directional Mobility by